© 2013 Professor Floyd Jay Winters, Web Master, CIW and ACA Certified
Adding Divs to a Webpage
![]() The
<div> tag is used to define a division or a section
of a web page such as the
masthead or the topNav
or the content or
the
footer.
This is usually done so the web page layout can be organized into logical
sections, and so each section can be consistently formatted with the same styles. A div is a block element.
Divs are usually defined within a stylesheet and they are used to establish the layout or skeleton of the body
or the page.
The
<div> tag is used to define a division or a section
of a web page such as the
masthead or the topNav
or the content or
the
footer.
This is usually done so the web page layout can be organized into logical
sections, and so each section can be consistently formatted with the same styles. A div is a block element.
Divs are usually defined within a stylesheet and they are used to establish the layout or skeleton of the body
or the page.
An Internal Stylesheet is used to give consistency to the layout, format, and tag properties on a particular Web page. An internal stylesheet is placed inside the <head> tags. It begins and ends with the <style> tag. You could declare the default font-family and color of all <h1> tags on a page within the stylesheet. And Div tags are almost always defined within a stylesheet. When a Div is defined in a stylesheet it is preceded by a # sign.
An External Cascading Stylesheet (CSS) is used to give consistency to the layout, format, and tag properties for an entire Web site. For instance, you could declare the default font-family and color of all <h1> tags on a site. External Cascading Stylesheets should be the primary place to set virtually all of your Div definitions.
The HTML source code below shows a webpage that uses Divs which have been
defined in an Internal Stylesheet and are then used in the body of the page.
Notice how the Divs organize the body of the page and also how they are nested.
Notice how the Divs are preceded by a #
sign when it is defined in the stylesheet.
Notice how the Divs are
referenced by
id="DivName" in the body of the web page.
Note: When using HTML5, the <footer> element would be used instead of <div id="footer">
Click here to see the actual display of the page below:
(You
can easily copy the code below, paste into Notepad, and then modify it.)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Very Simple Div Demo</title>
<style
type="text/css">
body {width:700px; margin:auto; margin-top:8px;
background-color:#B3D0FA} /* center */
h1 {color:#369}
/* set existing tag attributes first */
#wrapper {background-color:white}
/* define Divs
second; they start with a # */
#masthead
{background-color:#369; color:white; font-size:24px;
height:58px;
text-align:center}
#content
{background-color:white; padding-left:48px; padding-right:48px}
#footer {background-color:#369;
color:white;
font-size:12px; text-align:center; padding:8px}
</style>
</head>
<body>
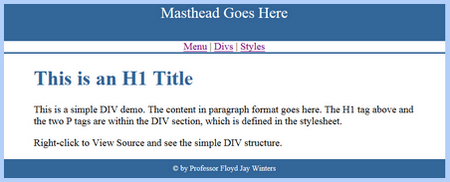
<div id="wrapper">
<div id="masthead">
Masthead Goes Here<br>
</div>
<!-- close masthead -->
<div id="content">
<h1>This
is an H1 Title</h1>
<p>This is a simple DIV demo.
The content in paragraph format goes here.
The H1 tag above and the two P
tags are within the DIV section,
which is defined in the stylesheet.</p>
<p>Right-click
to View Source and see the simple DIV structure.</p>
</div> <!-- close content -->
<div id="footer">
© by Professor Floyd
Jay Winters
<br>
</div> <!-- close footer -->
</div> <!-- close
wrapper -->
</body>
</html>
Click to see the actual
display of the page above:

To add a horizontal navigation bar, insert the line below under the
#masthead definition in the stylesheet:
#topNav {border-bottom:2px solid #369;
text-align:center}
Then insert the lines below under the
masthead div in the body:
<div id="topNav">
<a href="Menu.htm">Menu</a> |
<a href="Divs.htm">Divs</a> |
<a href="Styles.htm">Styles</a>
</div>
Click to see the actual page with the horizontal navigation links:
For more HTML code samples see: www.w3schools.com
For other resources and tutorials see: quackit.com and htmlquick.com
ValidateValidate
Validation checks the syntax of your file, looking for both errors and possible issues when viewing your page in a browser. Some of the problems reported are missing end tags, missing characters, invalid attributes, incorrect nesting of elements...
your file, see: http://validator.w3.org
Review Assignment Learning Project: 10 Practice Review Steps